Email Reporting
The Email Reporting feature helps your Help Desk and IT team respond to user issues more quickly and identify opportunities to improve system security. You can access the feature by clicking Reporting in the EAS navigation menu.
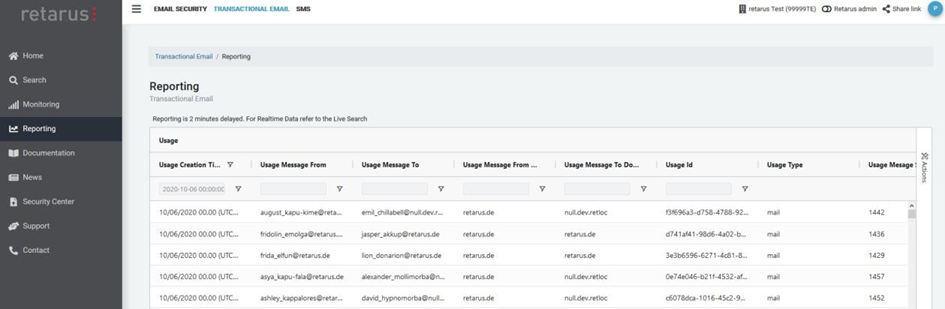
With EAS Reporting, you can create custom reports for the past 45 days and download them as CSV or Excel files.
📌 You can request a daily report in
.csvformat by opening a Service Request.
Data in User Data Report (UDR)
Column name | Description | Possible values |
|---|---|---|
Processing domain | Indicates which Retarus datacenter processed and sent the message. | DE1, DE2, US1, US2, SG1, CH1 |
Status Details | Provides more detailed information about the final status of a message after processing. | VALIDATION_ERROR, INVALID_ADDRESS, FORBIDDEN_RECIPIENT, PROCESSING_FAILED, SUPPRESSED, PREVIOUSLY_BOUNCED, OK, HARD_BOUNCE, SOFT_BOUNCE |
Entry interface | Indicates the entry interface used to submit the message to the Transactional Email service. | rest, smtp |
Status | Gives general information about the final status of the processed message. | OK, ERROR |
Status Code | The SMTP status response code received by Transactional Email MTAs (Mail Transfer Agents). | See full list: SMTP response codes documentation |
Substatus | Used to group messages according to the three main expected outputs after submitting a JobRequest. | DELIVERED, BOUNCED, DROPPED |
Tenant | Indicates which tenant the Transactional Email Technical Account is assigned to. | multiple |
Technical Account | The Technical Account ID under which the message was processed. | multiple |
SMTP status codes
Code | Meaning |
200 | Nonstandard success response (see RFC 876 for details) |
211 | System status or a system help response |
214 | Help message |
220 | <domain> Service ready |
221 | <domain> Service closing transmission channel |
250 | Requested mail action completed successfully |
251 | User not local; message will be forwarded to <forward-path> |
252 | Cannot VRFY user, but will accept message and attempt delivery |
354 | Start mail input; end with <CRLF>.<CRLF> |
421 | <domain> Service not available, closing transmission channel |
450 | Requested mail action not taken: mailbox is unavailable |
451 | Requested action aborted: local error occurred during processing |
452 | Requested action not taken: insufficient system storage available |
500 | Syntax error: command not recognized |
501 | Syntax error in parameters or arguments |
502 | Command not implemented |
503 | Invalid sequence of commands |
504 | Command parameter not implemented |
521 | <domain> does not accept mail (see RFC1846 for details) |
530 | Access denied |
550 | Requested action not taken: mailbox is unavailable |
551 | User not local; please try <forward-path> |
552 | Requested mail action aborted: storage allocation exceeded |
553 | Requested action not taken: mailbox name is not allowed |
554 | Transaction failed |
The status codes above are provided by the recipient’s mail servers. Although SMTP status codes follow a standardized framework (RFC 3463), Internet Service Providers (ISPs) and mail servers may implement and interpret them differently.
