Message Signing
Message Signing feature overview
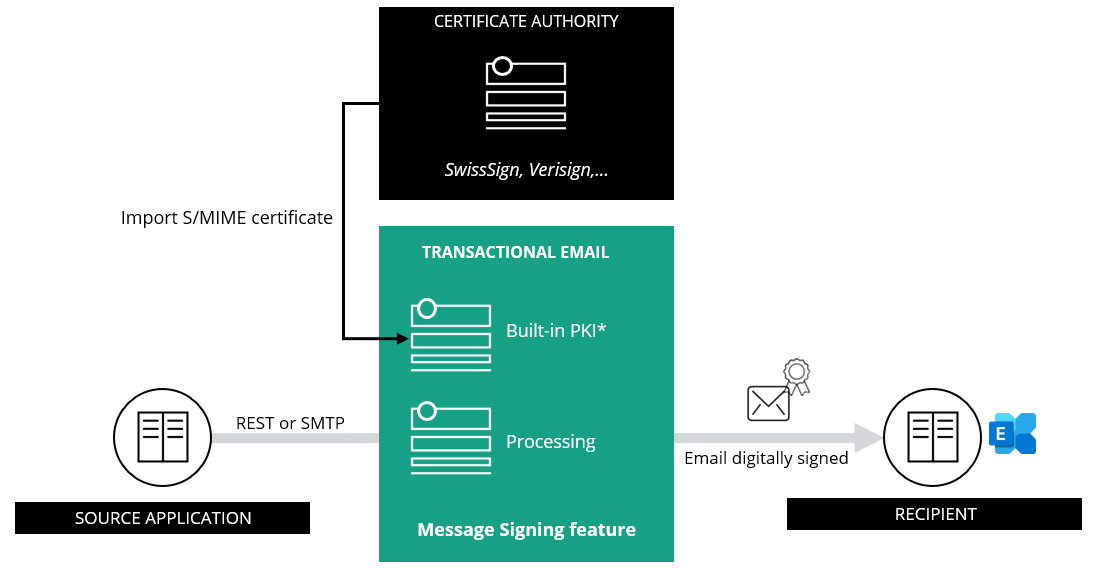
The Message Signing feature offers you the ability to digitally sign emails sent out by your company’s applications. This digital signature attached to your outbound email adds an extra layer of security by providing confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity. As a result, organizations increase both trust and awareness of their application email messages by providing assurance to the recipient that the content of the email legitimately comes from your organization.
*Public Key Infrastructure
Message Signing feature is only available for the German datacenters for the moment.
What is a digital signature?
A digital signature is used to authenticate and protect communication across the Internet by verifying the message has been sent by that named sender. This to protect both sender and recipient from unauthorized access and phishing attempts. Adding a digital signature enhanced integrity, authenticity and commitment for Applications outbound emails:
integrity: check that the message has not been altered or tampered with;
authenticity: the message does in fact come from the sender;
commitment: the sender should not be able to deny having written it.
By creating a unique digital fingerprint, digital signatures provide the highest level of security assurance by verifying the signer’s identity. This is done through a trusted third party, known as a Certificate Authority (CA).
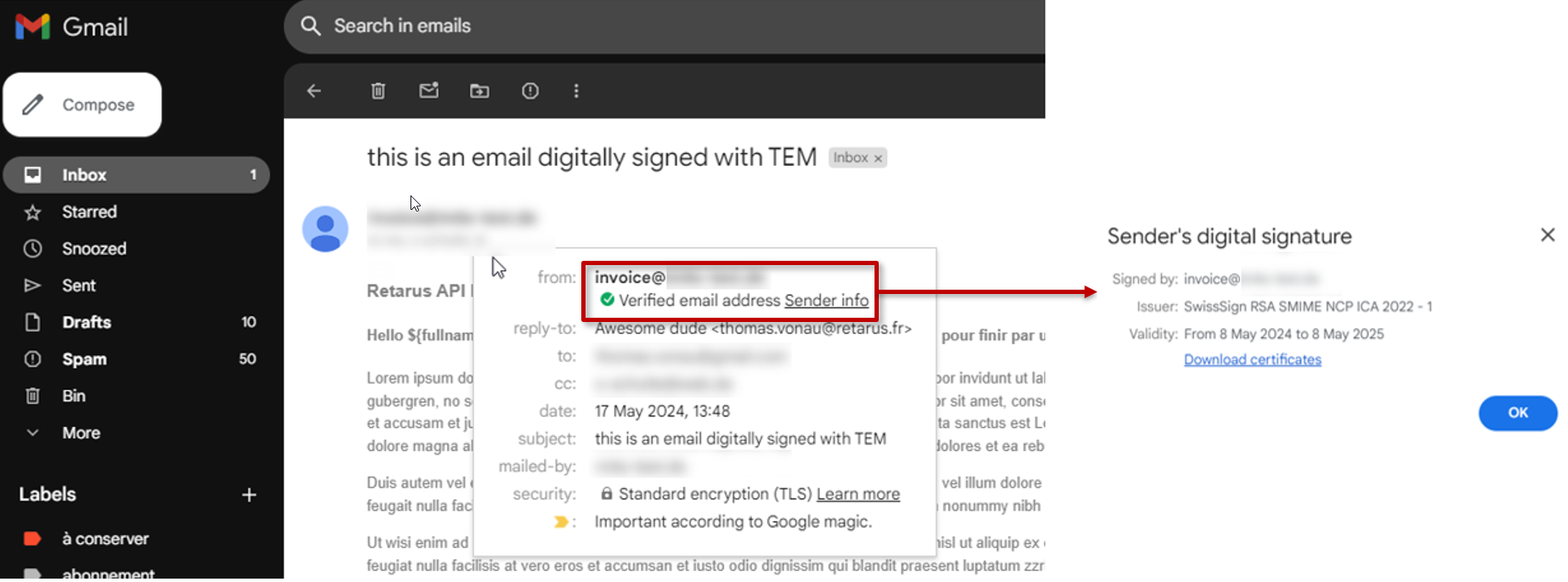
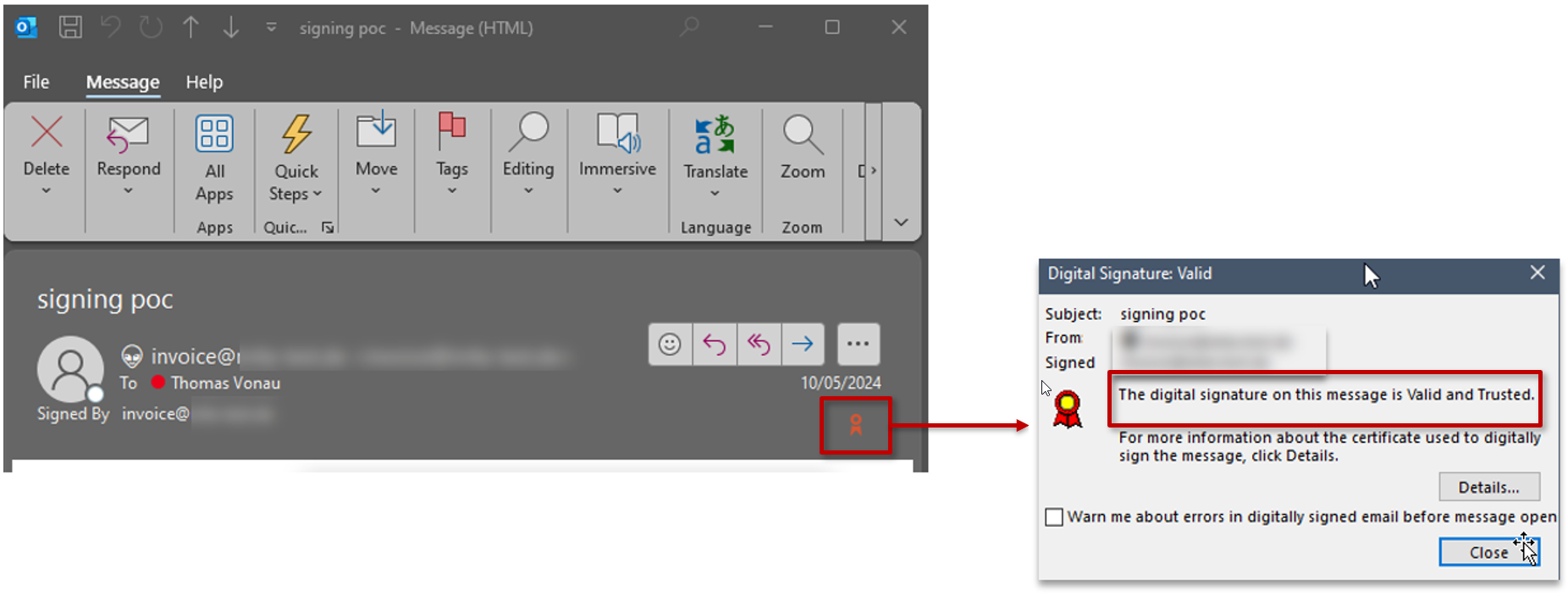
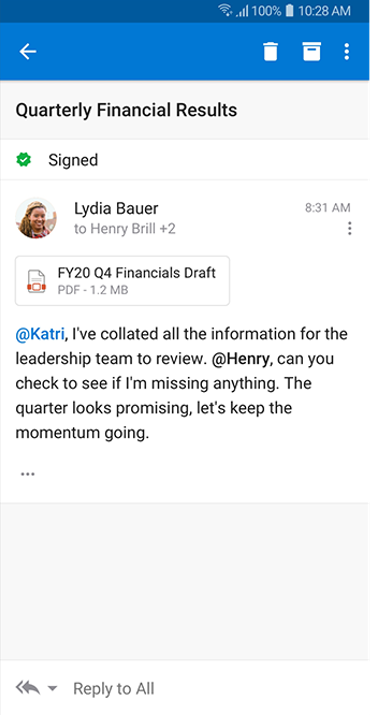
How a digitally signed email looks like?
Requirements
Technical integration requirements
Message Signing feature booked and configured for at least one Transactional Email Technical Account
Technical Account configured for data processing in german datacenters only
Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (S/MIME) certificate only, delivered by a Certificate Authority (also known as “paid certificate”)
For PGP or self-signed certificate, please contact our Technical Consultant team to qualify the potential integration.
Recipient requirements
Most of the mailbox providers integrate a built-in S/MIME certificate reader. For users accessing their emails through a webmailer, they might need to ask their administrator to install an additional extension.